Cardiac arrest, heart attacks and stroke are serious matters and they can happen to anyone at any time. Being aware of the various risk factors can help to considerably lower your risk of suffering from any one of them.
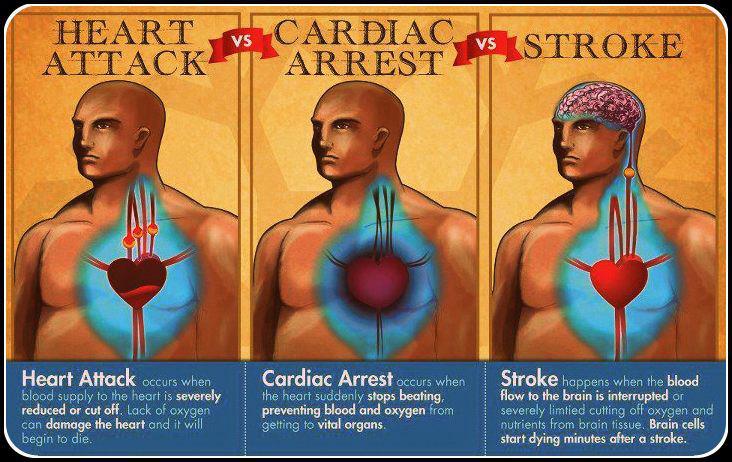
Cardiac Arrest: Electrical System Gone Haywire
Cardiac arrest happens when the heart muscles suddenly stops beating due to the organ’s malfunction. When the electrical system in the heart goes haywire, it causes an irregular heartbeat and even complete cessation of the pumping action of the heart. Cardiac arrest causes signs such as gasping, absence of breath and unresponsiveness. If someone goes into cardiac arrest and fails to get immediate treatment, they can die in a matter of minutes.
Heart Attack: Restriction of Blood Flow
Heart attacks happen when one or more regions of the heart fails to get oxygen due to restriction of blood flow. A heart attack causes symptoms such as pressure, tightness or squeezing in the chest, pain that radiates to the arms, shoulders, upper back and jaw, shortness of breath, cold sweats, nausea, and anxiety.
Stroke: Severe Reduction of Blood Supply to Brain
A stroke can happen when a part of the brain fails to get oxygen because of the cessation or severe reduction of the flow of blood to the vital organ. Some of the symptoms of a stroke include sudden severe headache without any known triggering factors, dizziness, loss of coordination, confusion, trouble with speaking, and numbness or weakness of the face or one side of the body.







